Resources > Blog > 46> Automated vs Manual Accounts Payable workflow: Key differences
Automated Vs Manual Accounts Payable Workflow: Key Differences
What is the Accounts Payable Workflow?
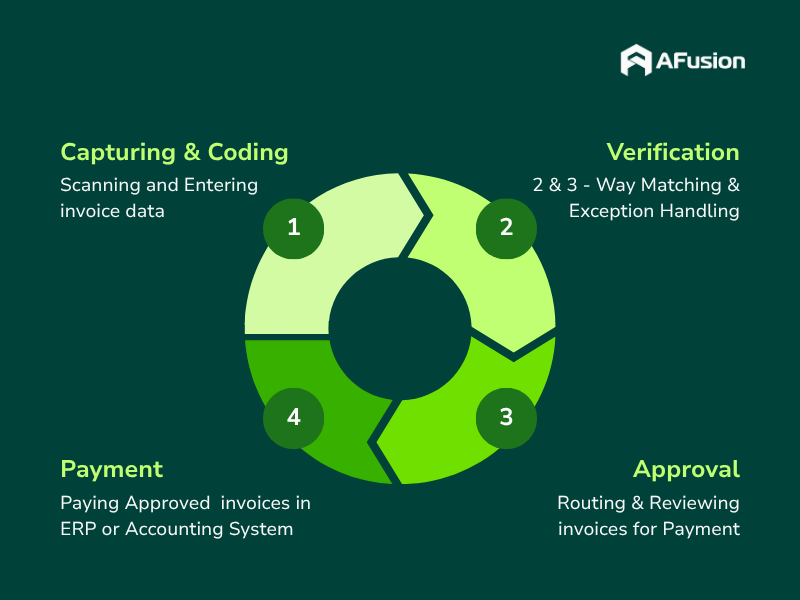
Automated Vs Manual Workflow: A Comparison
Below, we analyze each step in the AP workflow, comparing automated vs manual approaches and highlighting the advantages automation brings.
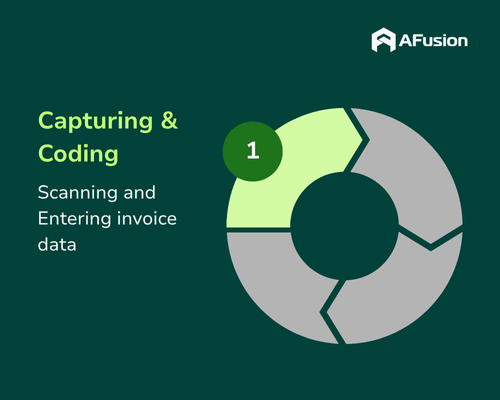
Step 1: Capturing and Coding Invoices
Standard Process:
In a manual workflow, when invoices arrive (via email, mail, or fax), AP staff manually enter invoice details into the ERP system or accounting software. This includes invoice numbers, supplier names, item details, prices, total amounts due, taxes, and payment terms. For complex transactions, staff may need to cross-reference multiple purchase orders (POs) or partial invoices, increasing the workload.
Issues:
This step highlights a significant difference between automated vs manual processes. Manual invoice capture is time-consuming and prone to errors. Mistakes in data entry, such as incorrect amounts or miscoding, can lead to duplicate invoices or incorrect payments. Additionally, invoices may get lost if not sent to the correct address or processed slowly, resulting in late payment penalties and strained supplier relationships.
Automation Solution:
Automated AP solutions leverage optical character recognition (OCR), intelligent document processing (IDP), and machine learning to scan, code, and digitize invoices upon receipt. Paper or PDF invoices are converted into digital data, and information is automatically entered into the ERP system. These systems also provide a dedicated email address for suppliers to send invoices, reducing the risk of loss. This approach saves time, minimizes data entry errors, and ensures accurate data from the outset.
Step 2: Invoice Verification
Standard Process:
After invoices are entered into the ERP system, AP staff must reconcile invoice details with purchase orders (POs) and delivery receipts to confirm that goods or services were delivered as agreed. This process, often called account payable 3 way matching, requires thorough checks to identify discrepancies, such as incorrect quantities or prices. When comparing automated vs manual workflows, accuracy in matching remains critical to avoid payment errors.
Issues:
Manual three-way matching is time-intensive, especially with large invoice volumes or incomplete information. If a PO or receipt is missing, staff may need to contact other departments or physically verify inventory, slowing down the process. Moreover, selectively verifying only high-value invoices to save time can overlook errors or fraud in smaller invoices.
Automation Solution:
Automated AP solutions integrated with ERP systems can perform real-time three-way matching for every invoice. The system automatically compares invoice data with POs and receipts, flagging discrepancies for staff review. This accelerates verification, ensures thorough checks for all invoices, and reduces the risk of errors and fraud.
Step 3: Invoice Approval Process
Standard Process:
Once verified, invoices are sent to an approver (typically a manager or administrative director) for review and sign-off. In automated vs manual workflows, this step plays a crucial role in ensuring financial control and accountability. In manual workflows, this is often done via email or physical document handoff. The approver reviews the invoice based on criteria like accuracy or allowable expenses, then approves or rejects it.

Issues:
Manual approval processes often cause bottlenecks, especially when approvers handle large volumes of invoices. Approval emails may be overlooked, paper documents can get lost, and delays in approval lead to late payments. Additionally, overburdened approvers may approve invoices without thorough review, increasing the risk of incorrect payments.
Automation Solution:
Automated AP solutions demonstrate a clear distinction from manual processes by automatically routing invoices to the appropriate approver based on criteria like invoice amount or supplier type. The system sends reminders if approvals are delayed. Approvers can communicate with the AP team via a dashboard, minimizing delays and ensuring issues are resolved quickly. This reduces pressure on approvers and speeds up processing.
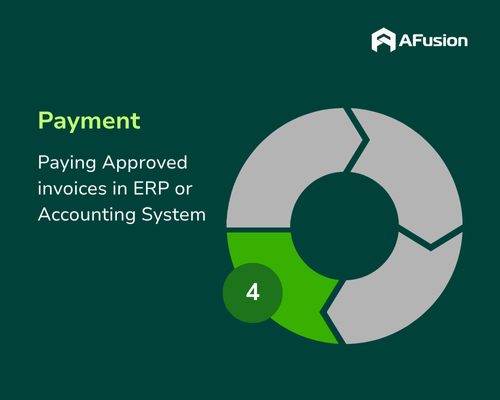
Step 4: Payment Processing
Standard Process:
After approval, invoices move to the payment stage. In manual workflows, AP staff prepare payment batches, consolidating approved invoices and organizing them by payment method (check, ACH transfer, or credit card). Payments are then sent to a controller or CFO for final approval before execution.
Issues:
Manual payment processing is time-consuming and duplicate invoice payments, particularly for complex payments like partial invoices. Printing and mailing checks is costly and increases fraud risks. Transitioning suppliers to electronic payments (e.g., ACH) can be challenging without an efficient supplier management system. Multiple payment methods also add complexity, requiring separate processes.
Automation Solution:
The difference in payment processing between automated vs manual workflows lies in integration. Automated systems consolidate payment methods into a single platform, simplifying electronic payment processing. These systems also facilitate transitioning suppliers to electronic payments, reducing costs associated with paper checks. Automated payments sync with ERP systems, eliminating manual data entry and ensuring accurate transaction recording. This saves time, reduces errors, and enhances financial efficiency.
Tips and Tricks to Improve Your Accounts Payable Workflow
- Centralize Communication: Instead of relying on scattered emails, calls, or texts, implement a centralized communication platform. Automated AP solutions provide dashboards to track and store all invoice-related communications, ensuring no information is missed. Integrate with ERP: Choose an AP automation solution that seamlessly integrates with your ERP system. This ensures accurate data sharing across departments, reducing errors and improving transparency.
- Integrate with ERP: Choose an AP automation solution that seamlessly integrates with your ERP system. This ensures accurate data sharing across departments, reducing errors and improving transparency.
- Strengthen Internal Controls: Implement controls like segregation of duties to prevent fraud and errors. Automated AP solutions can enforce these controls automatically and provide a comprehensive audit trail.
- Leverage Early Payment Discounts: Build strong supplier relationships and take advantage of early payment discounts. AP automation enables faster invoice processing, allowing you to capitalize on cost-saving opportunities.
- Monitor Supplier Performance: Use AP system data to track supplier performance, identifying duplicate or inaccurate invoices. Regular communication with suppliers helps resolve potential issues proactively.
- Track Invoice Processing Times: Establish clear timelines for each AP workflow step, from data entry to payment. Monitoring these timelines ensures timely payments and prompt resolution of errors.



 Next Post
Next Post



